
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, affects millions of people around the world. This article will cover the key aspects of this condition. It will look at what causes it, what symptoms it has, and how to manage it. By understanding eczema better, people can find ways to live with it more comfortably.
Defining Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis is the most common type of eczema. It affects both kids and adults. It’s a chronic condition that often comes with allergies, asthma, or hay fever in the family.
People with atopic dermatitis have flare-ups. During these, their skin gets very dry, red, and itchy.
Types of Eczema
There are more types of eczema besides atopic dermatitis, including:
- Contact dermatitis: This happens when the skin reacts to irritants or allergens like chemicals, soaps, or fabrics.
- Seborrheic dermatitis: This affects the scalp, face, and oily body areas. It causes scaly, flaky, and sometimes greasy patches.
Knowing the different types of eczema helps in finding the right treatment and managing it well.
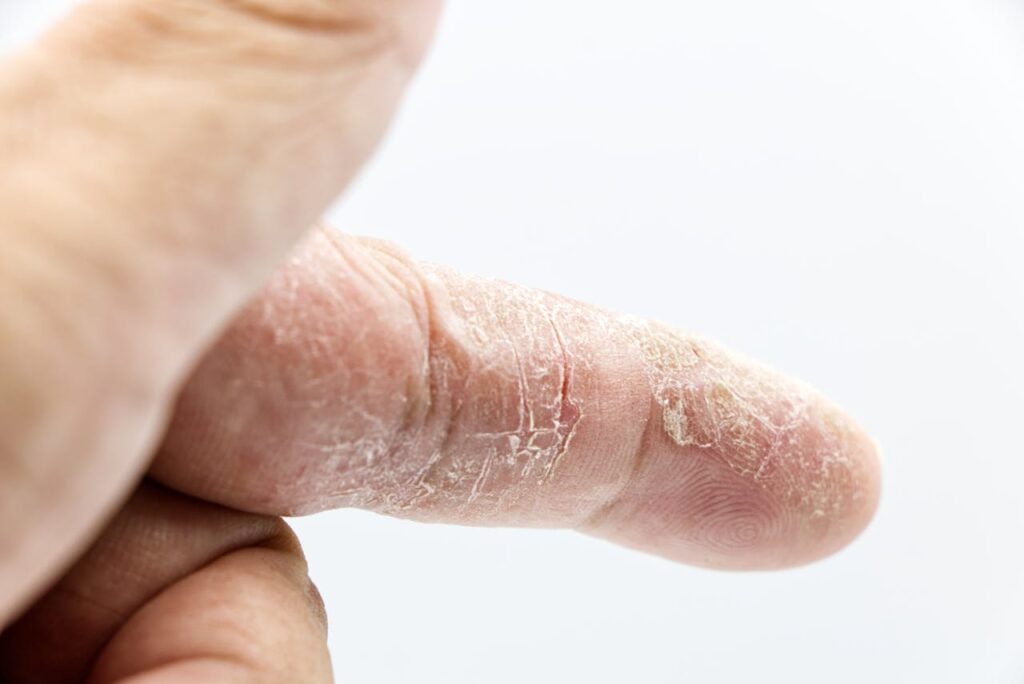
Causes of Eczema
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a complex condition with many factors playing a role. Knowing what causes eczema helps in managing it and preventing flare-ups. The main causes are genetic factors and environmental triggers.
Genetic Factors
Eczema has a strong genetic link, with certain genes making it more likely to happen. If your family has eczema, you’re more likely to get it too. This is because of genes that affect the skin’s barrier and immune system
Environmental Triggers
Environmental factors also trigger eczema. Common triggers include:
- Irritants like harsh soaps, detergents, and certain fabrics that can disrupt the skin’s natural barrier
- Allergens like dust mites, pollen, and pet dander that can cause an immune system overreaction
- Stress and anxiety, which can make eczema worse by affecting the body’s inflammatory response
- Changes in temperature and humidity that can lead to dry, irritated skin
Avoiding these triggers can help manage eczema symptoms and prevent flare-ups.

3 Of The Best Hyaluronic Acid Products for Eczema
For those with eczema, finding the right skincare products is key to managing symptoms and improving skin health. Several hyaluronic acid products are great for eczema. They use hyaluronic acid to hydrate and repair the skin. They also add soothing ingredients to help eczema-prone skin.
The CeraVe Renewing Facial Serum is a top choice for eczema. It’s fragrance-free and has hyaluronic acid and ceramides. These ingredients help keep moisture in and strengthen the skin’s barrier. People with eczema love how it reduces inflammation and makes their skin look better.
The The Ordinary Hyaluronic Acid 2% + B5 is another great option. It’s affordable and gives a strong dose of hyaluronic acid and vitamin B5. This combo deeply hydrates and calms irritated skin.
The Cetaphil Pro Eczema Calming Body Wash is ideal for eczema. It’s gentle and doesn’t have sulfates. It uses hyaluronic acid, colloidal oatmeal, and ceramides to clean and nourish the skin. This helps eczema sufferers find relief.
Adding hyaluronic acid to your skincare routine can really help with eczema. These products tackle dehydration and barrier damage. They also calm inflammation and help heal the skin, making it healthier and more resilient.

Eczema Symptoms
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, shows many visible signs that can really affect someone’s life. It’s important to know these signs to spot and handle this ongoing skin issue well.
Red, inflamed skin is a key sign of eczema. The affected spots can look raw, swollen, and irritated, often with a red color. This redness can come with a lot of itching, which can be hard on both the body and mind for those with eczema.
Dry, flaky skin is another common sign of eczema. The skin can get very dry, causing thick, scaly patches. These dry, cracked areas can be very uncomfortable and may get more irritated or infected.
- Red, inflamed skin
- Intense itching
- Dry, flaky skin
Sometimes, eczema leads to skin rashes. These can look like small, red bumps or big, weeping spots. These rashes can be really tough and might need special medical help to get better.
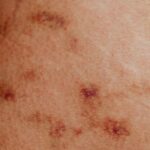
Contact Dermatitis
Eczema is a chronic skin condition that comes in many forms. Contact dermatitis is a common type that happens when the skin reacts to irritants or allergens. This leads to a red, itchy rash. Allergic eczema is a type of contact dermatitis that needs more attention.
Allergic Eczema: When the Skin Reacts
Allergic eczema, or allergic contact dermatitis, happens when the skin reacts to something it shouldn’t. This can be from everyday items like metals, chemicals, personal care products, or even some plants. The skin gets inflamed, making it red, itchy, and sometimes blistered.
- Identifying Triggers: Common causes of allergic eczema include nickel, latex, fragrances, and preservatives in cosmetics, jewelry, and other items.
- Avoiding Irritants: It’s important to avoid known triggers to manage allergic eczema. Reading labels carefully and choosing hypoallergenic products can help reduce exposure.
- Seeking Professional Help: If it doesn’t get better or is very bad, seeing a dermatologist is a good idea. They can give specific treatment and advice to soothe the skin and prevent more problems.
Understanding contact dermatitis and allergic eczema helps people take steps to manage it. This way, they can have healthier, more comfortable skin.

“Knowing, identifying and avoiding triggers is key to managing allergic eczema and keeping it under control.”
Seborrheic Eczema
Seborrheic eczema, also known as seborrheic dermatitis, affects the scalp, face, and oily body areas. It’s a type of eczema with a red, scaly, and sometimes itchy rash. This rash can be hard to manage.
This condition is caused by too much oil in the skin, a fungus called Malassezia, and genetics. It often comes back and needs a special way to handle it.
Symptoms of Seborrheic Eczema
The main signs of seborrheic eczema are:
- Greasy, yellow or white scales on the scalp, often called “dandruff”
- Red, inflamed skin on the face, especially around the eyebrows, nose, and chest or back
- Itchy, flaky skin that’s hard to control
- Rashes that keep coming back and can get worse during stress or weather changes
To manage seborrheic eczema, you might use medicated shampoos, creams, or ointments. You also need to make lifestyle changes to tackle the causes and triggers.

Diagnosing Eczema
Getting a correct diagnosis of eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is key for good treatment. Doctors use a detailed check-up and sometimes allergy tests to diagnose it.
Medical Evaluation
A doctor, like a dermatologist or primary care physician, will look closely at the patient’s skin during an evaluation. They check the rash’s look, feel, and pattern to see if it’s like eczema. They also consider the patient’s health history, including allergies or things that might trigger eczema.
Allergy Testing
Sometimes, doctors suggest allergy tests to find out what might be causing the eczema. These tests, like skin prick tests or blood tests, can spot specific allergens. Knowing these can help make a treatment plan that works and prevents more outbreaks.
By using a detailed check-up and sometimes allergy tests, doctors can accurately diagnose eczema. This helps them make a plan to tackle the root causes and symptoms.

For those facing eczema’s discomfort and frustration, there is hope. Treating eczema often means using both medication and lifestyle changes. Doctors can create personalized plans to ease symptoms and stop flare-ups.
Prescription drugs are key in managing eczema. Topical creams like hydrocortisone or triamcinolone reduce inflammation and calm the skin. For worse cases, oral or injectable steroids might be needed.
Immunomodulators, such as tacrolimus or pimecrolimus, work on the immune system to help control eczema. Sometimes, biologic drugs are used to treat the condition at its source.
Last but not least, along with medicine, changing your lifestyle can help with eczema. Keeping a regular skincare routine and using gentle products helps prevent flare-ups. Using moisturizers and emollients daily helps keep the skin hydrated and protected.
Stress management, like relaxation exercises or mindfulness, can also help. Stress is a common trigger for eczema.
